
Application software is a vital part of our everyday tech use, helping us accomplish a variety of tasks from work to play. But what exactly is application software, and what are the different types available? Let's break it down.
What is Application Software?
Application software, or simply an app, is designed to help users perform specific tasks. These tasks can be as varied as writing a document, managing a project, or editing a photo. Unlike system software, which manages the hardware and basic operations of a computer, application software provides tools that directly benefit the user.
Types of Application Software
There are several types of application software, each serving different purposes:
Productivity Software
Productivity software helps users create documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and manage emails. Examples include:
Microsoft 365: This suite includes Word for document processing, Excel for spreadsheets, PowerPoint for presentations, and Outlook for email management.
Google Workspace: Offers cloud-based tools like Docs, Sheets, Slides, and Gmail, allowing for seamless collaboration.
Web Browsers
Web browsers are essential for accessing the internet. They allow users to visit websites, run web applications, and more. Popular browsers include:
Communication Tools
Communication software enables users to connect and collaborate, whether for personal use or in professional settings. Key examples are:
Media Players and Editors
Media software allows users to consume and create content. Examples include:
Spotify and Apple Music for streaming music.
Adobe Photoshop for photo editing.
Final Cut Pro for video editing.
Project Management Software
These tools help teams plan, track, and manage projects efficiently. Common examples are:
Custom Web Applications
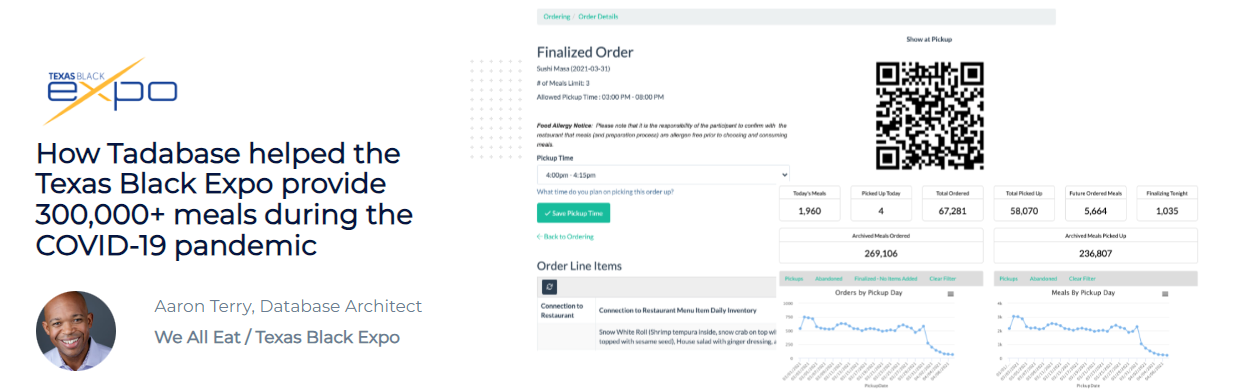
Custom web applications are built to meet specific business needs without the need for extensive coding. One notable example is: Tadabase: Tadabase allows businesses to create custom applications to manage operations effectively. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, Tadabase helped the Texas Black Expo provide over 300,000 meals by efficiently managing resources.
Choosing the Right Application Software
When selecting application software, consider the following factors:
1. Functionality: Does the software meet your specific needs?
2. Usability: Is the software easy to use?
3. Compatibility: Will it work with your existing systems?
4. Scalability: Can it grow with your needs?
5. Cost: Is it within your budget, considering both initial and ongoing expenses?
Benefits of Application Software
 Using the right application software can offer numerous benefits:
Using the right application software can offer numerous benefits:
Increased Efficiency: Automates routine tasks, saving time and effort.
Enhanced Accuracy: Reduces the likelihood of errors.
Improved Collaboration: Facilitates teamwork, especially in remote settings.
Better Decision-Making: Provides data and insights to inform decisions.
Conclusion
Application software is essential for enhancing productivity, communication, and overall efficiency. By understanding the different types of application software and carefully choosing the right tools, you can significantly improve your personal and professional activities.
FAQ
Q: What's the difference between an app and an application?
A: The terms "app" and "application" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences, especially in a business context:
App: A software designed for a single purpose or function, often associated with mobile devices. Apps are typically used for personal purposes and are not critical for business operations. They are built with a mobile-first approach and are not designed to handle complex business processes.
Application: A more comprehensive software that performs a range of related functions. Applications are crucial for business functionality as they often form the backbone of business operations. They are designed to be used across various devices, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices, and serve both personal and business needs.
Key Differences Between Apps and Applications:
| Feature | App | Application |
| Purpose | Single function | Multiple related functions |
| Importance | Not critical for business | Critical for business operations |
| Device | Mobile-first | Used across multiple device types |
| Usage | Primarily personal | Both personal and business |
Q: What distinguishes on-premise software from hosted software?
A: On-premise software and hosted software differ primarily in their deployment and management:
On-Premise Software:
- Installed and operated from your organization's own servers.
- Managed and maintained by your internal IT team.
- Involves upfront costs for licenses and ongoing expenses for maintenance.
- Highly customizable to fit your specific business requirements.
Hosted Software (SaaS):
- Delivered and managed remotely via the cloud by a service provider.
- Subscription-based pricing, often based on user count or usage.
- Provider handles updates, security, and maintenance.
- Quick to deploy and easy to scale as your business needs change.
| Feature | On-Premise Software | Hosted Software (SaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Own servers | Cloud (remote servers) |
| Management | Internal IT team | Service provider |
| Cost Structure | Upfront licensing + maintenance | Subscription-based (per user/usage) |
| Customization | High | Limited |
| Deployment Speed | Slower (requires setup) | Fast (ready to use) |
| Scalability | Requires infrastructure investment | Easily scalable |
Which one should I choose for my business?
Opt for on-premise if you need complete control over your data and systems, and have the resources for upkeep.
Choose hosted (SaaS) for a flexible, cost-effective solution that's quick to start and easy to scale.
Q: What's the difference between application software and an application platform?
A: Application software and application platforms serve different roles:
Application Software:
- A standalone program designed for end-users, performing specific tasks like word processing, spreadsheet management, or web browsing.
- Examples include Microsoft Word, Excel, and Google Chrome.
Application Platform:
- A suite of tools and services that provide the necessary infrastructure for application software to run.
- Supports applications in various environments, from individual devices to large-scale cloud deployments.
- Typically includes an operating system, execution services, data services, cloud services, and development tools.
| Feature | Application Software | Application Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specific end-user tasks | Infrastructure for running applications |
| Examples | Word processors, spreadsheets, browsers | Operating systems, cloud services |
| Scope | Single program | Group of software and services |
How does Tadabase fit into this?
Tadabase is an application platform that enables users to create custom application software solutions with ease. Our low-code platform provides the necessary tools for rapid application development, empowering users to implement changes and enhance efficiency without deep technical expertise. We believe that those most affected by application software should lead its development, as they have the clearest understanding of their needs. Start your free trial today!
Q: How is system software different from application software?
A: System software and application software serve different functions within a computer system:
System Software:
- The foundational software that manages the hardware components of a computer and provides a platform for running application software.
- Examples include operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, which coordinate between the hardware and various applications.
Application Software:
- Programs designed to perform specific tasks for users, such as word processing, spreadsheet analysis, or web browsing.
- Examples include Microsoft Word for document creation, Excel for data analysis, and Google Chrome for internet browsing.
In essence, system software serves as the backbone of a computer, enabling the smooth operation of application software, which in turn provides specific functionalities to the user.
Q: What steps should I take to choose the right application software for my needs?
A: Choosing the right application software involves several key steps:
1. Conduct a Needs Assessment:
- Engage with stakeholders including managers, colleagues, partners, and providers to understand the specific problem the software needs to address.
- Identify the tasks and processes the software should improve and determine the target users.
2. Consider Key Factors:
Functionality Needed: Ensure the software has the features required to meet your objectives.
Implementation: Plan how the software will be deployed, including the rollout strategy and training approach.
Support: Check the level of support provided by the vendor for troubleshooting and assistance.
IT Infrastructure: Assess the compatibility of the software with your existing IT environment.
Global Expertise: If applicable, ensure the software can support operations across different regions.
Pricing & ROI: Evaluate the cost of the software against the expected return on investment.
3. Decide on Implementation Approach:
- Determine whether a phased or all-at-once implementation is more suitable for your organization.
- Consider factors like the scale of deployment, the need for organized training, and the measurement of success.
4. Leverage Resources:
- Utilize available resources such as how-to videos and tutorials to gain a better understanding of the software and its capabilities.
By following these steps, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your organization's needs and goals.
Published by



